Corporate Social Responsibility
Table of Contents
Contrary to traditional view firms’ have
expanded the scope of the purpose of doing business and not only considered the
profits but also work for the betterment of society and communities. This study
tires to explore the firms’ Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) with respect
to firms’ goals and objectives and how these strategies affect different
stakeholders. Moreover, evaluations of potential impacts of such strategies are
also discussed.
Corporate
social responsibility (CSR) is becoming the heart of strategic management and
researchers are devoting their attentions to analyze the impacts of such CSR strategies
to organizational goals and objectives. Literature has evidenced a number of
studies that try to explore the construct in respect of organizational strategy
over the last 60 years. Bowen (1953) studies hundred largest businesses having
power with respect to the affects of their actions and decisions on
individual’s lives and tried to explore the social responsibilities of business
executives. After that Davis (1960) expended the concept of CSR and suggests
that CSR are firms’ actions and decisions ahead of their direct economic benefits
for social betterment. Moreover, in 1990s researchers studied CSR in respect of
alternative themes like corporate citizenship, business ethics theory or stakeholder
theory.
However,
today the concept of CSR is seen into broader term and researchers have been
expended its scope into new dimensions. According to CMI corporate social
responsibility is defined as ways of doing business while ensuring social
responsibilities and also being answerable for the affect of corporate
operations on society. Furthermore, CIPD defines CSR into broader term as
compliance with corporate governance practices, doing business in ethical ways,
considering economical, environmental and social affects on human rights and
more importantly they expand the context of stakeholders to social partners and
also included overseas employees contrary to traditional view of stakeholders. Wikipedia
defined CSR strategy into three aspects given below.
1. CSR strategy should monitor and ensure
conformity to local and international laws, norms and ethical issues.
2. Consider and squeeze the accountability of
impacts of their actions on all stakeholders including environment.
3. Voluntarily take a part in public
interests through eradicating potential public impairments irrespective of
legal issues.
So,
in conclusion CSR practices are beyond the direct benefits of organizations and
consider wider social aspects in different perspectives while executing
business operations ethically. However, though these CSR strategies didn’t
provide direct benefits but still these strategies comply with firms’
objectives. Porter & Kramer (2006) suggest that firms’ CSR strategies
significantly contribute to the value creation in both primary and secondary
activities. They map social responsibilities with respect to value chain model.
They identify CSR activities for both inbound logistics and outbound logistics
in this respect that illustrate relationship of CSR activities and firms’
operations. Moreover, Tripathi & Petro (2010) also demonstrate constructive
affects of firms’ CSR strategies to its value chain and lead to sustainable
competitive advantage. This implies that CSR strategies usually comply with
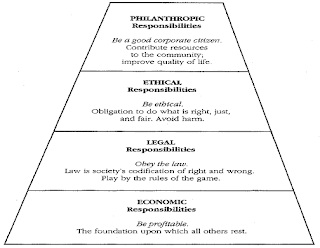
firms’ objectives. Moreover, Carroll (1991) also demonstrates the nature and
pyramid of CSR activities as shown in the figure 1. On the other hand it is
also argued that firms follow CSR practices not due their genuine concern to
social benefits but association of such CSR strategies to firms’ performances
(Banerjee, 2007).
Fig 1: Carroll (1991) Pyramid
of Corporate Social Responsibility
Firms’
CSR strategies not only contribute to firms’ objectives but also affect its
stakeholders in different ways. It is found that communicating CSR strategies
lead to positive responses from their stakeholders (Maignan & Ferrell, 2001).
With more exposure to the social and ethical aspiration, firms can attract
critical stakeholders’ attention positively (Vilanova, 2007). So, these results
demonstrate that stakeholders are affected by firms’ CSR activities and also
described by stakeholder theory that suggests that positive relations with
stakeholders create value for organization. Stakeholders can be defined as any
group that can affect or can be affected by firms’ decisions and objectives
(Freeman & Velamuri, 2006:12). Firms’ CSR activities positively contribute
to its performances and increase firms’ value that is the concern of its
shareholders (Spencer
and Taylor, 1987). For an employee perspective it is
important how his organization deals with ergonomics issues and provide physically
and emotionally healthy environment. Employee will suffer in stress and
pressure in the absence of such protections as stated by Cooper et al. (1998) who
suggest seven potential reasons that contribute to stress at workplace. Firms’
intensions to solve such issues as social responsibility beyond to its direct
interest positively affects on employee motivation. Customers are also
influenced and research reveals that seventy six percent of the customers
switched to those brand products or outlets that contribute significantly to
the benefits of society and community (Maignan & Ferrell, 2001).
Another comparative research proposed by these two reveals that forty percent
of households in US choose those brands that include corporate citizenship in their
business objectives (Maignan
& Ferrell, 2000).
On the other hand government and NGOs are also concerned with firms’
environmental policies. These statistics demonstrate the responses of firms’
stakeholders with respect to firms’ intentions to the benefits of society and
environment. Following diagram by CMI illustrates some examples that how
different factors including heat and ventilation affects employee
performance.
Fig
2: CMI (2010) Elements of Influence Diagram
Pakistan
Petroleum Limited (PPL) produces 30 percent of total Gas production in
Pakistan. Company has successfully managed environmental issues to protect
society. Company has also developed PPL welfare trust with the consultation of
its stakeholders that work for the betterment of people and trust is involved
in numerous projects of education, healthcare activities and developing
infrastructure for Pakistani people. Stakeholders are also involved that
motivate them towards organization commitment in this respect (CSR cases, 2011).
Organizations
have their own goals and objective and provide input in developing strategies
to meet those objectives. It is important that firms’ CSR strategies should
aligned with organizational strategies. Aligning means that both strategies
should follow same principle and work as one. Firms have developed strategies
at corporate level, functional level and business level. Even each department
set their own goals and plans their activities. In conclusion firms should
develop CSR strategies that ultimately fit organizational goals and objectives.
This can be done through vertical or horizontal alignment. Vertical alignment
makes certain that CSR strategy is applied from top-bottom hierarchy. On the
other hand horizontal alignment believes that all organizational departments
and teams should collectively contribute to the firms’ social responsibility. Porter
& Kramer (2006) have developed model that illustrate that how CSR
strategies can be aligned for both primary and secondary activities.
The
Boeing is biggest giant that produces jetliners and known from its better
quality airplanes. In order to achieve these goals Boeing implemented several quality
practices that support their workforce for better performance. Company has been
outsourcing many of its components. In order to coordinate company leveraged
their skilled workers to their suppliers to train them. Providing equal
employee opportunities regardless of any discrimination company successfully
implement code of basic working conditions and human rights to provide safe
working conditions to their employees and awarded by Human Rights Campaign
Foundation for providing best non-discriminatory workplace and got highest
Corporate Equality Index ranking contribute positively to employee motivation
that ultimately increase quality (Boeing,
2011).
Johnson
et al. (2010) have defined strategy into following words
“The direction and scope of an organization over the
long term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through its
configuration of resources with the aim of fulfilling stakeholder expectations”
In
short strategies provide guidelines and directions to achieve specific goals
and objectives. SMART and clearly communicated strategies allow managers to
make operational plans at each corporate, functional, business and departmental
levels. Moreover, these strategies also allow identifying CSR activities to be
performed while planning these operational plans. Prioritizing social issues
that need to be practiced clear the picture that needs to be solved in this
respect and allow constructing CSR strategy accordingly (Porter & Kramer,
2006). They proposed integrated model that combined generic social issues and
social dimensions that can contribute to firms’ competitiveness as shown in the
figure. Moreover, People, Profits and environment are key areas that should
cover in developing CSR strategies. National Refinery Limited (NRL) is the
largest petroleum refinery firm working in Pakistan. Company has clear
environment strategy according to the laws and achieves ISO 14001and OHSAS
18001 certifications in this respect. The milestone is gain by implementing
successful firm’s Occupational Health and
safety Management System and Environmental Management System that also
contributes to employee commitment and organizational objectives(CSR
cases, 2011).
|
Generic Social Issues
Social Issues that do not contribute significantly to its operations
and also not affect its long term goals and objectives
|
|
Value Chain &
Social Impacts
Social issues that can be affected from ordinary business
operations
|
|
Social Dimensions of
Competitive Context
Those External Social issues that affect
competitive drivers of a firm
|
Askari Bank Ltd. Provides financial services and is one of the leading players
of Pakistani financial industry. Bank contributes into various social
activities including poverty alleviation, health and medical sciences, women
and child care, education and human and scientific research. Bank also creates
AIDS awareness and water conservation to the people of Pakistan that contribute
to customer loyalty (CSR cases, 2011).
In conclusion developing CSR strategy a clear view of firm’s objective
is needed. After that prioritizing social issues that need to be solved and
contributes to firm’s competitiveness is also critical in this respect.
You
have developed very good strategic plans that clearly direct towards firms’
goals and objectives but all these efforts will be in vain if no proper
implementation is made in this respect. This section will study the processes
of effective and successful implementation of CSR strategies.
Figure
2 illustrates the relation of CSR activities and firms’ primary and secondary
operations as demonstrated in porter’s value chain model. Firms can use all
these CSR practices in their respective operations that will ultimately
contribute positively to the firms’ value and benefits of society and community
as well. Successful implementation of such CSR activities increases value at
each functional level and overall to the firms’ value. KASB group include KASB
securities, bank and capital and contributes significantly to the Pakistan’s
economy. Group has been working in four CSR areas. First the group trains their
employees to make them industrial leader through various training sessions and
secondly they share their policies countrywide that provide input for other
organizations in decision making they do so by providing research articles and seminars.
Group also take a part in to various developmental projects and at the end
promote sports activities and culture of Pakistan (CSR cases, 2011).
Implementing training programs group is successfully contribute to human
resource practices and quality of the product. Boeing collaborates with General
Electronics and Rolls-Royce in order to manufacture fuel efficient and
environment friendly engines and 787 dreamliner save 20% fuel than any other
same capacity airplane that increases the overall efficiency (Boeing, 787
Dreamliner). Moreover, company successfully implements six sigma lean
productions and brings CAD (computer added design) and CAM (computer added
manufacturing) that allows recognizing customers’ need and reduce time along
with more like hood of success of designing and manufacturing high quality
products according to their customers’ need.
After
identifying critical stakeholders, clear communication of firms’ CSR strategies
to all these stakeholders is vary critical for the successful implementation of
CSR strategy. For proper implementation
of CSR strategies companies have to identify their primary and secondary
stakeholders and the level of influence that they can impose to firms’
strategies. CMI (2011) has developed an influence matrix grid that illustrates
the phenomena.
This
implies that for the stakeholders having less power and high interest
communicating such strategies is critical for successful implementation. On the
other hand in case where stakeholders are influencing with high power and
interest is a typical situation. Involving them in their decision making and
communicating the potential benefits for society and for them as well can solve
the problem in this respect as in the case of Pakistan Petroleum Limited who involves
their strong stakeholders in decisions of trust they made for the benefits of
society.
After
setting vision and mission statement and constructing SWOT analysis that examine
internal and external environment to locate appropriate long term objectives,
managers devise an implementation plan to achieve those objectives efficiently
and effectively. Both strategic issues including break down strategic plans
into tasks and actions and operational issues including indentifying and
acquiring resources and managing risks should consider while making
implementation plans. Heathfield has suggested active support from senior
management in implementation, effective and clear upward and downward
communication to all the stakeholders and implementing plan through competitive
analyses as critical factors for successful and effective implementation of strategic
plans.
Project
Management Body of Knowledge PMBOK (2007) has suggested five stag process to
manage any project and can be used to devise implementation plan. These stages
are given below.
Initiation: set
goals and objectives that you want to achieve
Planning: Identify
list of actions and task that have to perform in order to those goals
Executing: Execute
those action plans after acquiring needed resources while clear and effective
communication is also critical for successful execution.
Monitoring: Keep monitoring expected and actual results and take corrective
action where actual results are significantly differs from expected yield.
Closing: Close
the project and analyze project progress for further project plans.
Nestle
Pure Life Pakistan providing pure bottled water to Pakistani nation. Company’s
objective is to provide quality nutritious foods to consumers for their better
health. Their logo “Good Food for Good Life”
demonstrates their intentions to provide quality food. They plan to make sure
the availability of quality water to all areas of country even at rural area
where infrastructure really creates problems. Company develops their supply
chain to make available pure water in those rural areas. Moreover, company also
invests PKR 87.2 billions rupees as aid during dreadful flood came in 2010. For
this purpose they provide food bags along with bottled water to those areas,
vaccines and veterinary for animals and help to re-cultivate their crops.
After
implementing CSR strategies evaluating its impacts is critical for the
subsequent CSR projects as it allows identifying deficiencies and efficiencies
of the process. Measuring the consequences of CSR can be in the form of
tangible, intangible, social impact and environment affects. This segment will
try to evaluate the end results of CSR strategies.
Brookes emphasis on the accountability of firms’
wide spending on CSR projects and argues that performances of such CSR
strategies should evaluate to know actual benefits form these social
investments. Usually organizations set their own measures of evaluation of
their CSR strategy. Internal measures include evaluating criteria set within
the organization. For example The Boeing provides equal employee opportunity
regardless of gender or race. In addition providing healthful working
environment increases employee commitment that lead to high quality. So their
positive HRM practices are the major reason of their success in providing high
quality products for their customers. Their collaboration with General
Electrics & Roll-Rayce manufactures fuel efficient engines at low cost. Boeing
also considers environmental issues and their plans are not that munch
dangerous to environment. Moreover, firms can evaluate their energy consumption
and energy saved. Extent of training programs also illustrates their CSR
efforts and post training performances of those employees with increased
productivity also demonstrates the effectiveness of CSR strategy in this
respect.
External
measures are also critical while evaluating the potential impacts of firms’ CSR
strategies. These impacts can be assessed in the form of reduced no. of
complaints from customers and extent of customers’ satisfaction in response of
firms’ CSR strategy. Moreover the benefits to society form business’ core
products and operations are also important while studying impacts of CSR
strategies. Nestle Pakistan Ltd provides quality bottled water and other
quality food items all over the country that fulfills nutritious needs of
people. On the other hand many firms arrange different entertainment programs like
Askari Bank Ltd. arrange squash tournament in Pakistan and Coke presents Coke
Studio music programs. Social affects of such activities on the life of people
also demonstrates the influences of these CSR strategies. Moreover, awards and
certificates from different social institutes also show the successful impacts and
contribution of firms’ CSR strategies to the community and society as well. Many
firms’ also invest in education sector as social investment. Providing quality
education to ordinary people and their post qualification contributions towards
the mankind evaluates the success scores of CSR investments in education.
The concept of CSR is emerging and researchers are
exploring new dimensions of CSR strategies. This implies that firms’ have to
change themselves according to the change in environment and new CSR concepts
emerged in this respect. For this purpose managers have to keep up to date with
change and take corrective measures accordingly. However, there is trade off
between sticking with CSR fixed and changed strategy as changed strategy can
confuse people about long term firms’ objectives while same strategy can miss
the opportunities. Business link provides framework to review firms’
performances and can also be used to reassess firms’ CSR strategy. Following
steps are proposed in this respect.
Market
Performance: How well you perform in term of
sales growth and what is your next target market
Product and
Service: Product life cycle for which your
product will provide required benefits to your customers
Operational
Matters: Quality, technology, processes or any
internal issue that leads to decreased performances.
Financial
Matters: firm’s capital structure and level of
sales and cash flow are assessed.
Organization and
People: Organizational structure and HRM related
issues.
Applying these step in the context of CSR strategy
provide chance to review CSR strategy and refresh CSR strategy if needed.
Another approach that can be use is
Plan-do-review-revise approach. First stage of plan demonstrates the priorities
of plans for improvement while second stage of do implement the chosen plan and
assist people to achieve better performance. At Review stage we try to
understand the potential impact of those implemented strategies and at revise
stage we learn from our actions. Following diagram illustrate that how one can
implement Plan-do-review-revise approach for CSR strategy.
First you have to closely monitor issues regarding
CSR. For this purpose information can be collected from various newspapers,
magazines and journals as useful source of information. At second stage review
CSR strategies in the light of collected information and implement revised strategies
in this respect. At last evaluate the actual impacts of CSR strategy against
expected results. However, this process doesn’t stop here but starts again and
firms review their strategies and change according to the environment.
Banerjee,
S. B. (2007), “Corporate Social Responsibility: The Good, the Bad and the
Ugly”, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, UK
Boeing Company (2011), Boeing in brief,
[online] available at http://www.boeing.com/companyoffices/aboutus/brief.html
Bowen
H. R. (1953), “Social Responsibility of the Businessman”, New York: Harper
& Row
Carroll
A. B. (1991), “The Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility: Toward the Moral
Management of Organizational Stakeholders”, Business Horizons
CSR Cases
(2011), “Case studies: CSR in Pakistani perspective” [online]
available at
Cooper
C.L., Cooper R.D. & Eaker L.H. (1988), “Living with stress”, Penguin
CPID, “Corporate Social
Responsibilities”, [online] available at www.cipd.co.uk/subjects/corpstrtgy/corpsocres/csrfact.htm?IsSrchRes=1
Davis
K. (1960), “Can Business Afford to Ignore Social Responsibility?”, California
Management Review, Vol. 2(1):70-76
Freeman,
R. E. & Velamuri, S. R. (2006), “A New Approach to CSR: Company Stakeholder
Responsibility”, in A Kakabadse & M Morsing (eds), Corporate Social
Responsibility: Reconciling Aspiration with Application, Palgrave MacMillan,
Basingstoke, Hampshire
Johnson G., Scholes K.,
& Whittington R. (2010), “Exploring Corporate Strategy”, Pearson
Nestle (2011), “Nestle
Pakistan” [online] available at
Maignan
I & Ferrell O. C. (2000), “Measuring Corporate Citizenship in Two
Countries: The Case of the United States and France”, Journal of Business
Ethics, vol. 23(3):283-297
Maignan
I. & Ferrell O. C. (2001), “Antecedents and Benefits of Corporate Citizenship:
An Investigation of French Businesses”, Journal of Business Research, vol.
51(1):37-51
Porter
M. E. & Kramer M. R. (2006), “Strategy and Society: The link between
competitive advantage and corporate social responsibity”, Harvard Business
Review,
Spencer
B. A. and Taylor G. S. (1987), “A within and between analysis of the
relationship between corporate social responsibility and financial
performance”, Akron Business and Economic Review, Vol. 18:7-18
Tripathi
S. & Petro G. (2010), “Evolving Green Procurement and Sustainable Supply
Chain Practices in the Organizations: A Framework to Align Functional Strategy
Implementation to Organization’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Objectives”, Management Convergence, Vol. 1(1):24-33
Vilanova
L. (2007), “Neither Shareholder nor Stakeholder Management: What Happens When
Firms are Run for their Short-term Salient Stakeholder?”, European Management
Journal, vol. 25(2):146-162




Very informative post..
ReplyDeleteCSR NGO In India
ReplyDeleteThank you for your post. This is excellent information. It is amazing and wonderful to visit your site.
sap corporate social responsibility services
ReplyDeleteThank you for your post. This is excellent information. It is amazing and wonderful to visit your site.
emc software vendors
bmc software vendors
Microsoft goldpartner
sap crm service providers